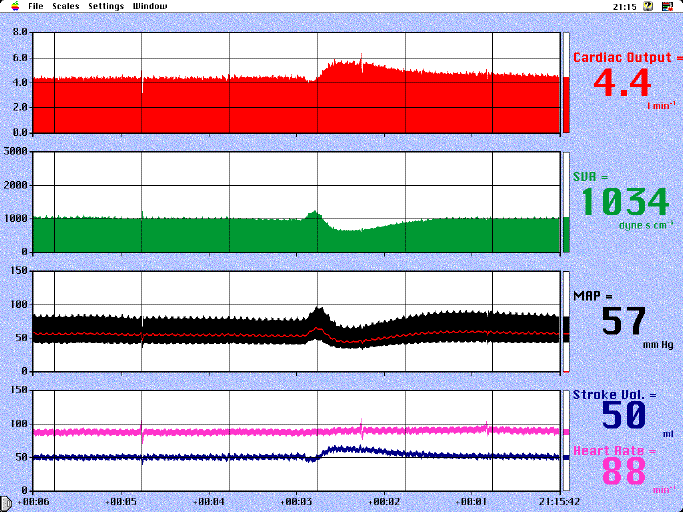

Adrenaline
The screen display shows the effect of an intravenous dose of adrenaline (5 mcg) given about 30 s before the change in blood pressure. There is a small increase in blood pressure due to vasoconstriction and it then falls below the starting value. This fall is due to a reduction in SVR (probably due to vasodilatation in muscle) which is only partially compensated for by the increase in stroke volume and cardiac output.
For an example of the effect of adrenaline on arterial pressure waveform - click here.